
Experiencing anxiety or imbalance is a regular occurrence in our contemporary swift-moving world. A large number of us grapple with these emotions, oblivious that the solution could be concealed within our own nervous system regulation.
Techniques of respiration such as the 4-7-8 method have exhibited efficacy in tranquilising the nervous system and reducing tension. This piece presents a manual on balancing your nervous system employing basic techniques and alterations in lifestyle.
You will acquire methods to enhance your wellbeing, both physically and emotionally. Prepare yourself to achieve equilibrium.
Understanding the Nervous System

The nervous system is an intricate network of nerves and cells which are responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body. Its primary components include the brain, spinal cord, and a vast network of sensory receptors throughout the body.
The nervous system plays a vital role in regulating bodily functions such as heartbeat, breathing, digestion, and movement.
Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system has a key role in our interaction with the environment, consisting of various interconnected elements.
- Central Nervous System (CNS) – The brain and spinal cord function as the command centre.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Incorporates nerves branching out from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
- Neurons – The fundamental units that transmit signals throughout the system.
- Dendrites – They receive messages from other cells and relay them to the cell body of the neuron.
- Axons – These transport electrical impulses from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
- Synapses – The minute gaps between neurons where neurotransmitters transmit messages.
- Neurotransmitters – These chemicals transport messages across synapses to other neurons or cells.
- Sensory Neurons – These identify external stimuli like touch, smell, and sound, sending data to the CNS.
- Motor Neurons – Convey directions from the CNS to muscles, triggering them to contract or relax.
- Nervous Tissue – Constitutes the organs of the nervous system, promoting internal communication.
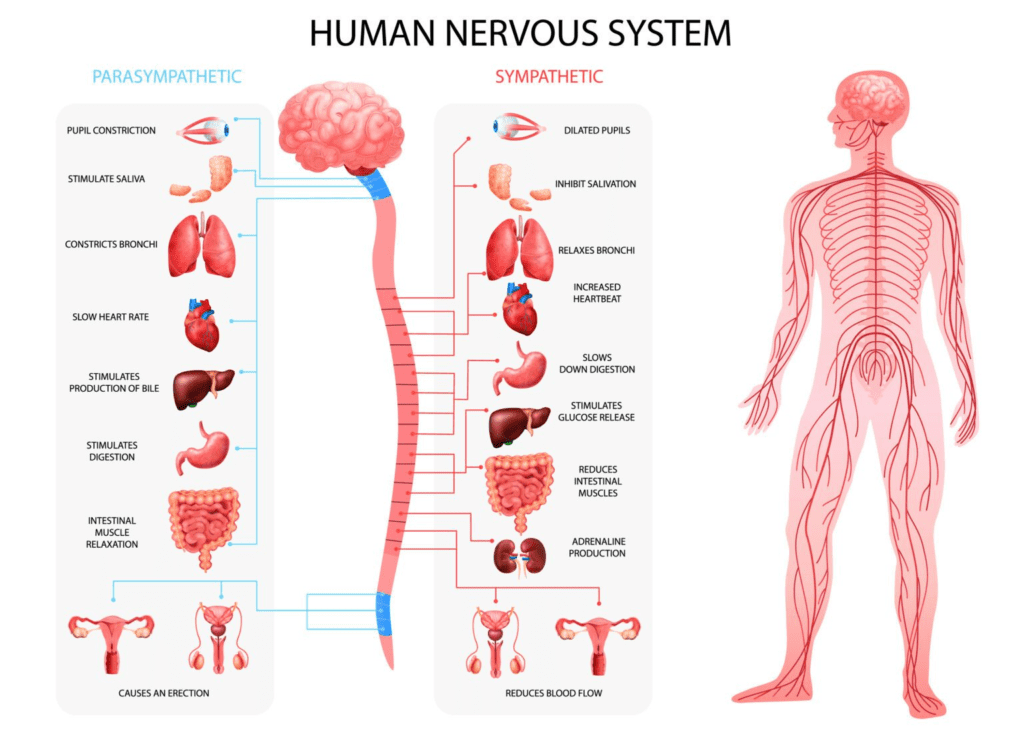
- Autonomic Nervous System – Manages automatic functions like heartbeat and digestion, with sympathetic and parasympathetic systems responsible for activation and relaxation respectively.
- Enteric Nervous System – Overseeing every phase of digestion, from swallowing to nutrient absorption to waste disposal.
Each component plays a significant function in maintaining our body’s equilibrium and facilitating appropriate responses to diverse situations and stresses in our surroundings.
Role of the Nervous System in Bodily Functions
Our nervous system holds a pivotal role in the conduct of our bodies. It governs every bodily function and responds to variations both within and beyond the body. This system serves as the controlling hub for all our actions, thoughts and reactions.
Correct operation of this system signifies our efficient stress management.
Sustained stress hampers the usual operation of our nervous system. Such maladaptation might contribute to anxiety, depression, unpleasant relationship results, and adversely influence overall wellbeing.
Sustaining the equilibrium of our nervous system is thus vital for superior health and contentment.
Importance of Nervous System Regulation
Maintaining a balanced nervous system is essential for overall health and well-being. Self-regulation and homeostasis play vital roles in ensuring the proper functioning of the nervous system.
Maintaining Balance for Overall Health and Well-being
Attaining a balanced nervous system is fundamental to our comprehensive health and wellness. Such stability promotes our physical and mental health growth, enabling effective management of stress.
With the right guidance, we get better at controlling our feelings and can adeptly manage life’s unexpected pressures. Continued stress typically results in an overly-active sympathetic nervous system, which can then induce high blood pressure along with other health problems.
Procedures intended to soothe the nervous system improve mental wellness, as well as contribute meaningfully to physical health by controlling blood pressure. Setting up a routine comprising relaxation techniques, physical exercise, and nutritious diet supports the control of the nervous system.
This all-round method encourages a state of homeostasis where the body’s systems function in unison, reducing chronic stress hazard and heightening the quality of life.
Self-regulation and Homeostasis
Self-regulation and homeostasis serve to keep our body’s balance in check. The nervous system, with its two branches, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, plays a critical role in this concert.
When the sympathetic system propels us towards ‘fight or flight’, the parasympathetic system lulls us back into a calm ‘rest and digest’ mode. It is key to our health to maintain a harmonious interplay between the two.
If the sympathetic side gains too much control, it disrupts our balance, triggering a host of health problems.
Successfully regulating the nervous system bolsters our ability to adapt and contributes to emotional equilibrium. Approaches enhancing this regulation utilise the nervous system’s innate capacity to return to a balanced state.
For example, addressing and managing stress empowers the parasympathetic side, counteracting the harmful excessive activation of the sympathetic branch. This even-handed activation promotes both physical and emotional wellness by encouraging an optimal state of physiological equilibrium, crucial for effective day-to-day functionality.
Techniques for Optimising Nervous System Regulation
Moreover, specific yoga practices and physical postures can also contribute to regulating the nervous system.
Breathing Techniques for Stress Reduction
Breathing techniques play a pivotal role in reducing stress and promoting relaxation. They help regulate the autonomic nervous system, enhancing both emotional regulation and anxiety reduction. Here’s how you can use different methods to calm your mind and body:
- Try the 4-7-8 breathing technique to quickly promote relaxation. First, you inhale deeply through your nose for 4 seconds, hold that breath for 7 seconds, and then exhale slowly through your mouth for 8 seconds. This pattern helps reduce anxiety.
- Practice coherent breathing to improve heart rate variability. You need to breathe at a rhythm of about 5-6 breaths per minute. It balances the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
- Use physiological sighs to calm down rapidly. Take two quick inhales through the nose and then a long exhale through the mouth. This action soothes the sympathetic nervous system immediately.
- Engage in deep breathing exercises daily to maintain a steady mind-body connection. Focus on slow, deep breaths that fill your lungs fully before gently releasing them.
- Incorporate these practices into regular intervals throughout your day, especially during moments of high stress or anxiety, to keep your nervous system balanced.
By integrating these techniques into everyday routines, individuals can effectively manage stress levels and bolster their overall mental well-being.
4-7-8 Breathing Technique
The 4-7-8 breathing technique is a simple yet powerful method to calm the nervous system. Developed by Dr Andrew Weil, it’s often described as a “natural tranquilliser“. This involves breathing in quietly through the nose for 4 seconds, holding the breath for 7 seconds, and then exhaling forcefully through the mouth for 8 seconds.
Practising this regularly can lead to reduced anxiety, better sleep quality, and lower blood pressure and heart rate.
“It acts like a natural tranquilliser for your nervous system.” – Dr Andrew Weil
People around the world use this relaxation breathing method not just for stress relief but also as an effective strategy to improve sleep. The beauty of this calming breath practice lies in its simplicity and accessibility.
You don’t need any special tools or extensive training to start benefiting from it today.
Resonant or Coherent Breathing
Resonant or Coherent Breathing involves taking slow, deep breaths at a rate of 5-6 per minute. This technique enhances heart rate variability. It also stimulates the vagus nerve. Such stimulation promotes relaxation across the body.
Practising this method helps reduce stress effects and supports healing processes. People find it a useful way to manage stress in daily life. It fosters a mind-body connection that aids in autonomic nervous system regulation.
Physiological Sigh
The physiological sigh involves two quick inhales followed by a longer exhale. This technique is effective for reducing stress and aiding emotional regulation, enhancing oxygenation, and improving cognitive performance.
It can be valuable in optimising nervous system regulation and restoring balance to the mind and body.
By practising the physiological sigh, individuals can harness its potential to calm the nervous system and promote feelings of relaxation. The technique is a simple yet powerful tool that may be incorporated into daily routines to support overall well-being through intentional breathing practices.
Yoga and Physical Postures for Nervous System Regulation
Yoga practices reduce stress and promote balance in the nervous system. Specific yoga poses can help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation. Consistent practice of yoga fosters self-awareness and effective stress management.
- Incorporate standing poses such as Mountain Pose, Triangle Pose, and Tree Pose to improve body awareness, strength, and balance.
- Include seated poses like Seated Forward Bend, Bound Angle Pose, and Child’s Pose to encourage relaxation and release tension in the body.
- Integrate restorative poses such as Corpse Pose, Supported Bridge Pose, and Reclining Bound Angle Pose for deep relaxation and stress reduction.
- Engage in balancing poses like Warrior III, Eagle Pose, and Half Moon Pose to improve focus, concentration, and stability.
- Practice gentle inversions like Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose to prompt the relaxation response of the nervous system.
By incorporating these physical postures into a regular yoga practice, individuals can effectively regulate their nervous system for improved mental and physical well-being.
Yoga Therapy
Yoga therapy blends physical postures, breath regulation, and sound therapy to enhance relaxation and emotional balance. It uses specific yoga practices and asanas to balance the autonomic nervous system.
In addition, it alleviates symptoms such as anxiety through the integration of breath control, humming, chanting, and sound therapy to increase vagal tone.
By combining these techniques in a yoga-based practice, individuals can optimise their nervous system regulation for enhanced emotional well-being and stress reduction. For instance, when practising yoga therapy incorporating breathing exercises like the 4-7-8 technique or coherent breathing alongside physical postures can help restore balance in the body’s vital systems.
Specific Yoga Practices
Yoga exercises play a pivotal role in promoting nervous system health and overall well-being. These practices incorporate poses, stretches, and controlled breathing to restore balance within the nervous system.
By fostering relaxation, deep breathing, and reducing depressive symptoms and chronic pain, specific yoga techniques offer effective stress management strategies. Regular engagement in yoga also promotes self-awareness for individuals seeking to optimise their nervous system regulation.
Relaxation techniques integrated into yoga exercises not only aid in controlling stress but also enhance emotional regulation. The mind-body connection established through yoga encourages individuals to effectively manage chronic pain while embracing self-care strategies for improved wellness.
By practising controlled breathing techniques within a mindfulness framework, individuals can experience enhanced nervous system function and balance.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Nervous System Balance
Engaging in activities such as listening to music and laughter for relaxation, practicing progressive muscle relaxation (PMR), and using weighted blankets for calming effects can contribute positively to restoring nervous system balance.
For more insights on optimizing nervous system regulation, explore the full blog.
Listening to Music and Laughter for Relaxation
Listening to music and laughter can notably contribute to relaxation. Research indicates that engaging with laughter has been shown to improve the recovery process of the autonomic nervous system after stress.
Additionally, music is associated with decreased heart rate and improved recovery processes following stressful events. The act of laughing promotes feelings of joy and eases bodily tension, contributing to emotional wellbeing and overall mental health.
These simple activities offer effective ways to reduce stress, enhance relaxation, and promote emotional resilience.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
PMR is a stress reduction technique that involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body. Developed by Edmund Jacobson in the 1920s, this practice aims to link physical relaxation with mental relaxation.
Regular PMR practice has been shown to significantly reduce anxiety, stress, and depressive symptoms by promoting overall mind-body relaxation through the release of tension in muscles.
By consciously tensing and then relaxing various muscle groups, PMR triggers a deep physical state of relaxation which contributes to mental peace and calmness. This practice can be an effective tool in managing anxiety, promoting mental relaxation, providing tension relief, and contributing to better overall nervous system regulation.
Use of Weighted Blankets for Calming Effects
Weighted blankets, also referred to as anxiety-reducing or stress-relieving blankets, offer comfort by applying a gentle pressure akin to the feeling of a hug. This comforting pressure has been noted to stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, encouraging relaxation and aiding in alleviating symptoms associated with an overactive sympathetic nervous system.
Studies suggest that the use of these soothing weighted throws enhances sleep quality, making them advantageous for individuals seeking relief from anxiety and striving for improved overall well-being.
These relaxation-inducing bed covers also help in balancing the nervous system by providing a comforting embrace that aids in activating the body’s natural response for tranquility.
Furthermore, they have been proven to effectively reduce restlessness and enhance sleep patterns due to their capacity to promote deep touch pressure stimulation – guiding one into undisturbed rest.
Factors Contributing to Nervous System Dysregulation
Chronic stress, traumatic events, suboptimal sleep habits, an unhealthy diet, genetic factors, insufficient physical activity, inadequate social support, and environmental factors contribute to nervous system dysregulation.
The impact of these factors on the nervous system can be profound and may lead to various health issues if left unaddressed. Recognising and addressing these contributing factors is crucial for restoring balance to the nervous system and promoting overall well-being.
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress notably amplifies sympathetic nervous system activity, ultimately leading to high blood pressure, anxiety, depression, addictive behaviours, sleep disturbances, and low energy levels.
This persistent strain on the autonomic nervous system is particularly concerning due to its concomitant association with a range of adverse health effects. In addition, chronic stress tends to worsen symptoms of underlying conditions such as anxiety disorders and major depressive episodes.
It is essential to acknowledge that long-term exposure to chronic stress can have an adverse impact on overall physical health and psychological well-being.
Traumatic Events
Traumatic events can lead to increased activation in the nervous system, making it difficult to regain equilibrium. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) frequently encompasses maladaptive sensory reactions, resulting in issues such as heightened arousal and derealisation.
These trauma-related symptoms encompass challenges in regulating physiological arousal and emotions.
The influence of traumatic events on the nervous system can be substantial, causing dysregulation that impacts daily life and overall health. It is vital to comprehend these effects to offer suitable assistance and treatments for individuals who have undergone trauma.
Poor Sleep Habits
Inadequate sleep patterns, such as insufficient sleep and sleeplessness, can significantly disturb the functionality of the nervous system. This disturbance leads to a rise in stress hormones, which impedes the body’s ability to self-regulate.
Studies have demonstrated that chronic stress due to a lack of quality sleep not only impacts mental well-being but also adversely affects physical health.
Addressing poor sleep habits is vital for optimising nervous system regulation. Creating consistent bedtime rituals and participating in calming pre-sleep activities can crucially contribute to achieving this equilibrium and promoting better overall health.
Unhealthy Diet
Unhealthy diets, high in saturated fats and sugars, have an adverse impact on brain health and function. The prevalence of poor dietary management and sedentary lifestyles has contributed to a significant increase in obesity, with profound implications for brain health.
Moreover, research indicates that high-caloric diets exacerbate the effects of brain injury, escalating cognitive dysfunction.
These unhealthy dietary choices lead to neurobiological changes associated with unbalanced nutrition and pose an increased risk for neurological disorders, cognitive impairment, metabolic syndrome, and other conditions impacting brain health.
Furthermore, these dietary habits contribute to the ongoing obesity epidemic while also being linked to cognitive decline and the deterioration of overall brain health.
Diastasis Recti
Diastasis recti, a condition where the rectus abdominis muscles separate along the midline, can have significant implications for core stability and nervous system regulation. This separation weakens the abdominal wall, potentially leading to issues such as poor posture, lower back pain, and disrupted breathing patterns—all of which can influence how the autonomic nervous system (ANS) manages essential bodily functions.
The core muscles, particularly the rectus abdominis, play a crucial role in maintaining posture and supporting efficient breathing. When these muscles are compromised due to diastasis recti, the body may develop compensatory mechanisms that place additional strain on other systems, potentially affecting ANS regulation. For example, altered breathing patterns can impact the parasympathetic nervous system’s ability to promote relaxation and recovery.
Given these potential effects, it is important to understand how to check for diastasis recti. Early detection allows for timely intervention, helping to prevent further complications and maintain optimal nervous system function.
Genetic Factors
Hereditary factors play a significant role in nervous system dysfunction, influencing genetic predisposition and brain activation. Research indicates that mean brain activation during fear learning has an additive genetic influence of 0.34, demonstrating how genetic factors contribute to emotional regulation and stress response.
Furthermore, safety learning exhibits a higher genetic influence (_h__2_ = 0.55) compared to fear learning, emphasising the impact of hereditary traits on the nervous system’s ability to regulate responses and identify threats.
Genetic predispositions can impact an individual’s capacity for safety learning, fear conditioning, and emotional regulation. These insights emphasise the importance of understanding the genetic influences on nervous system regulation to develop tailored approaches for addressing dysregulation rooted in hereditary factors.
Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle, characterised by lack of physical activity, is a significant contributor to neurological disorders and dysfunction in the nervous system. It has been identified as a leading factor in cognitive decline and an increased risk for neurodegenerative diseases.
Statistics reveal that approximately one billion people globally are affected by the adverse impacts of insufficient physical activity on their nervous system health. Regular exercise plays a crucial role in enhancing cardiovascular fitness, stimulating cerebral circulation, and promoting the release of neurotrophic factors such as BDNF which can help mitigate risks associated with neurodegeneration and cognitive decline.
Research also shows that regular physical activity acts as a protective factor against the detrimental effects of a sedentary lifestyle on brain health and motor function. These findings emphasise the importance of incorporating physical fitness activities into daily routines to maintain optimal nervous system regulation.
Poor Social Support
Insufficient social support has an adverse impact on an individual’s ability to withstand stress and can lead to mental and physical health challenges. It is closely linked to heightened heart rate, increased blood pressure, and intensified physiological stress responses.
Long-term isolation also contributes to symptoms of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), highlighting the critical role of healthy social connections in maintaining overall well-being.
These effects underscore the necessity for robust social networks in promoting resilience against stressors and fostering mental and physical health.
Substandard social connections significantly elevate the risk of various mental health issues, including depression and PTSD symptoms due to intensified physiological stress responses.
Heightened heart rate and increased blood pressure are evident consequences of chronic isolation, emphasising the importance of quality social support as a protective factor for both mental and physical health.
Environmental Factors
Light exposure notably impacts the nervous system and plays a crucial role in regulating circadian rhythms. Studies have shown that exposure to natural light during the day can improve sleep quality, mood regulation, and overall well-being.
In contrast, inadequate light exposure, especially at night, can disturb circadian rhythms and lead to disruptions in sleep patterns which may impact stress responses.
Excessive noise pollution is another environmental factor that can negatively affect nervous system regulation. High levels of noise have been associated with elevated stress responses and increased cortisol levels, contributing to chronic stress.
This underlines the importance of assessing the impact of environmental factors such as light exposure and noise pollution on nervous system function for maintaining optimal health and well-being.
Conclusion
Restoring equilibrium to the nervous system is essential for overall health and well-being. Practices like breathing exercises, yoga therapy, and lifestyle adjustments play a vital role in regulating the nervous system.
Effective stress management and co-regulation techniques underline the importance of social interaction in maintaining a balanced nervous system. Optimising nervous system regulation through these practices activates its innate ability to restore harmony, benefiting both mind and body.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279390/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK217810/
- https://mindowl.org/nervous-system-regulation/ (2024-02-27)
- https://positivepsychology.com/nervous-system-regulation/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9381001/
- https://www.topdoctors.co.uk/medical-articles/optimising-the-autonomic-nervous-system-a-pathway-to-enhanced-health
- https://www.southendvirtualschool.co.uk/Pages/Download/a0d86362-596e-4250-bacf-a874532fbbce/PageSectionDocuments
- https://mfm.au/blog/breathing-your-way-to-better-health-the-benefits-of-the-4-7-8-technique
- https://www.rosalbacourtney.com/resonance-frequency-breathing/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334465001_Breath_Practices_for_Survivor_and_Caregiver_Stress_Depression_and_Post-traumatic_Stress_Disorder_Connection_Co-regulation_Compassion (2019-04-10)
- https://www.calm.com/blog/how-to-regulate-nervous-system
- https://www.heartandbonesyoga.com/resources/how-reset-and-regulate-your-nervous-system-through-yoga-and-movement/ (2024-10-24)
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6302464/
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/ways-to-lower-cortisol
- https://www.healthline.com/health/progressive-muscle-relaxation (2020-08-10)
- https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2022/march/weighted-blankets (2022-03-24)
- https://integratedlistening.com/blog/understanding-and-treating-a-dysregulated-nervous-system-signs-symptoms-and-rebalancing-techniques/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9720153/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3258094/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10057655/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8904491/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10442603/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4142018/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2921311/
- https://neurofit.app/learn/en/environment_nervous_system/
MindOwl Founder – My own struggles in life have led me to this path of understanding the human condition. I graduated with a bachelor’s degree in philosophy before completing a master’s degree in psychology at Regent’s University London. I then completed a postgraduate diploma in philosophical counselling before being trained in ACT (Acceptance and commitment therapy).
I’ve spent the last eight years studying the encounter of meditative practices with modern psychology.

